AV receivers play an essential role in home audio systems, and understanding their power capabilities is essential for understanding what you can expect with such a device.
The power of an AV receiver refers to its ability to deliver electrical energy to speakers, determining their output volume and overall performance. It is represented in watts per channel (WPC).
Having a clear understanding of power values helps users match their receiver’s power with the speakers’ requirements, ensuring compatibility and preventing underpowered or overloaded setups. In addition, higher power ratings generally result in louder and more dynamic sound reproduction, making it important to consider the room size and listening preferences.
However, it’s worth noting that power alone does not guarantee superior audio quality, as factors like speaker efficiency, room acoustics, and overall system synergy also play significant roles. Ultimately, comprehending the power specifications of AV receivers empowers users to make informed decisions when building their audio setups, ensuring a balanced and immersive sound performance that suits their needs and preferences.
In this article, I’ll talk about the power behind AV receivers. I’ll closely examine the system of measuring power output and consider common misconceptions about AV receiver power ratings.
Watts: measuring power output

Watts serve as the main metric to measure power output. Understanding this parameter enables you to gauge the amplifier’s capabilities accurately. By delving into this topic, you will raise your knowledge to a new level, which will help you use the entire multimedia system more correctly.
Definition and significance of watts
Watts are a unit of measurement used to quantify power, specifically the rate at which energy is consumed or produced.
In the context of audio equipment, watts measure the power output of devices such as AV receivers, amplifiers, and speakers. They indicate the electrical energy that these devices can deliver to generate sound. The significance of watts lies in their ability to determine the loudness and overall performance of audio systems. Higher wattage generally translates to greater power and volume, allowing for louder and more dynamic sound reproduction.
RMS vs. peak power
RMS (Root Mean Square) power and peak power are two terms used to describe different aspects of power output in audio equipment.
RMS power refers to the continuous, sustained power that a device can deliver without distortion. It provides a more accurate representation of the average power output.
On the other hand, peak power represents the maximum power output that a device can handle for short durations, typically during dynamic sound peaks.
While peak power showcases the device’s capability to handle brief bursts of high-energy signals, RMS power is a more reliable indicator of the device’s sustained performance.
Understanding the difference between RMS and peak power helps users make informed decisions when choosing audio equipment based on their specific needs and preferences.
How wattage affects audio quality and performance
The receiver wattage of an audio device plays one of the most important roles in determining its overall audio quality and performance.
Wattage directly relates to the power output of the device, which in turn affects various aspects of sound reproduction. Higher wattage generally leads to greater volume capabilities, allowing the device to produce louder sounds without distortion.
Additionally, higher wattage provides better control over speakers, resulting in improved clarity, accuracy, and dynamic range.
Channels: distribution of audio signals

Understanding the channelization of AVRs is of paramount importance in audio reproduction. AV receivers can be categorized into two main types: multi-channel and stereo receivers. Let’s consider them in more detail:
- Multi-channel receivers support various channel configurations, such as 5.1, 7.1, etc., representing the number of speakers and subwoofers in the setup. These configurations offer immersive audio experiences by distributing audio signals across multiple channels, creating a realistic soundstage.
- On the other hand, stereo receivers are designed for two-channel audio reproduction and are ideal for simpler setups or music-focused listening.
Choosing the appropriate receiver and understanding its channelization capabilities ensures that the audio signals are properly distributed, resulting in accurate and engaging sound reproduction.
How many watts per channel do I need for my receiver?
Several factors come into play when considering the wattage per channel for your AV receiver. I suggest you consider them in more detail:
- Firstly, it depends on the size of your room and the desired listening volume. For smaller spaces or moderate listening levels, a receiver with around 50-80 watts per channel would suffice. However, larger rooms or a preference for louder volumes may require receivers with 100-200 watts per channel or more.
- It’s also essential to consider the sensitivity of your speakers, as more efficient speakers require fewer watts to produce the same volume.
Ultimately, it’s best to strike a balance between your room size, speaker sensitivity and desired listening experience when determining the ideal wattage per channel for your AV receiver.
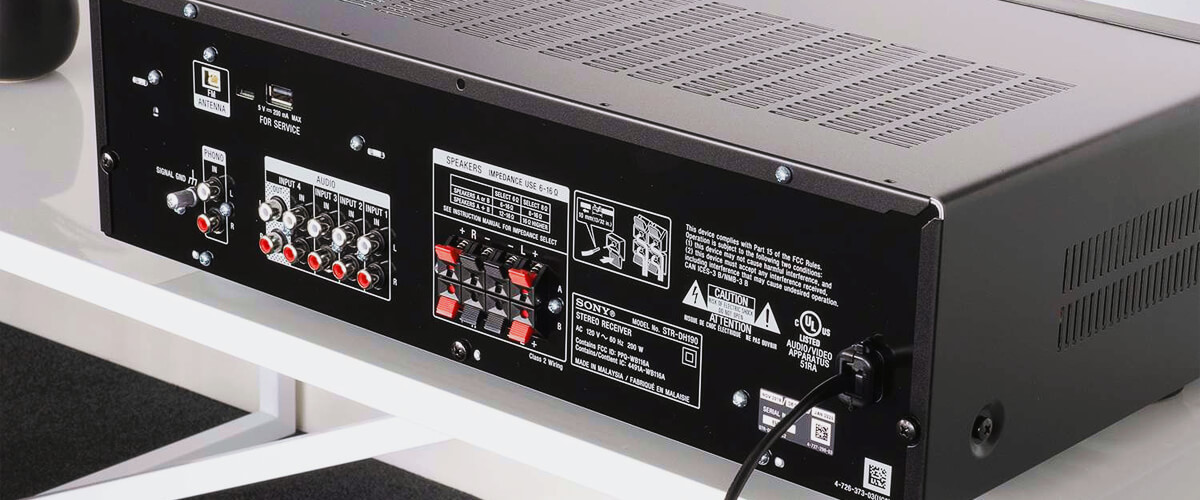
Impedance: electrical resistance and load
Impedance is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering, playing an important role in audiovisual (AV) systems. Acting as electrical resistance and load, it determines the harmony between your speakers and amplifier. Now I suggest you understand this topic in more detail.
Basics of impedance and its role in AV systems
It refers to the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to alternating current (AC) flow. Impedance matching is essential for optimal power transfer between components. If the impedance is mismatched, it can lead to power loss, distortion, or even damage to the equipment. To ensure proper impedance matching, you should carefully select speakers and amplifiers with compatible impedance ratings.
Understanding the basics of impedance enables technicians to design and set up AV systems that deliver high-quality audio reproduction and avoid potential issues associated with impedance mismatch.
Matching speaker and receiver impedance
Matching speaker and receiver impedance is an essential aspect of electrical systems, specifically in the realm of audio transmission. Impedance refers to the electrical resistance encountered when a current flows through a circuit. In the context of speakers and receivers, properly matched impedance ensures efficient power transfer and prevents signal distortion.
Mismatched impedance can lead to reduced audio quality, overheating, and even damage to the equipment. However, carefully selecting speakers and receivers with compatible impedance ratings allows the electrical energy to flow smoothly, delivering pristine sound reproduction.
Сommon misconceptions about AV receiver power ratings
Now I will debunk the power rating myths and shed some light on what really matters when evaluating the performance of an AV receiver.
High wattage equals better sound quality
One common misconception in AV receiver power ratings is the belief that higher wattage automatically translates to superior sound quality. However, this notion is far from accurate.
While power is undoubtedly an essential factor, it is not the sole determinant of audio performance. Aspects such as speaker efficiency, room size, and listening aspects play significant roles.
Buying the most powerful receiver may lead to unnecessary expenses and potential overkill for the intended setup. A more prudent approach involves matching the receiver’s power output to the speakers’ requirements, taking into account the desired listening experience.
By doing so, one can achieve optimal sound quality without unnecessary power excess. Quality over quantity prevails when it comes to sonic bliss.
Power ratings and real-world performance
It’s important to understand that AV receiver power ratings alone do not solely determine the performance and sound quality of your system.
While power is a factor, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. The true performance of your receiver is influenced by various factors like speaker efficiency, wire quality, room acoustics, speaker placement, and a number of other options.
A high-powered receiver doesn’t guarantee better sound if paired with inefficient speakers or low-quality wires. Conversely, a lower-powered receiver can deliver exceptional performance with efficient speakers and optimal setup.
So, when evaluating AV receivers, consider the holistic picture, focusing on the synergy of components rather than solely relying on power ratings.
Importance of other specifications
Instead of fixating solely on wattage, consider factors like impedance compatibility, signal-to-noise ratio, frequency response, and distortion levels.
These specifications determine the overall audio quality, system compatibility, and ability to drive speakers effectively. Impedance compatibility ensures optimal power transfer, while the signal-to-noise ratio affects the clarity of sound reproduction. Frequency response indicates the range of frequencies a receiver can handle accurately, while low distortion levels contribute to cleaner, distortion-free audio.
By considering these specifications alongside power ratings, you can make an informed decision and select an AV receiver that meets your audio needs precisely.













